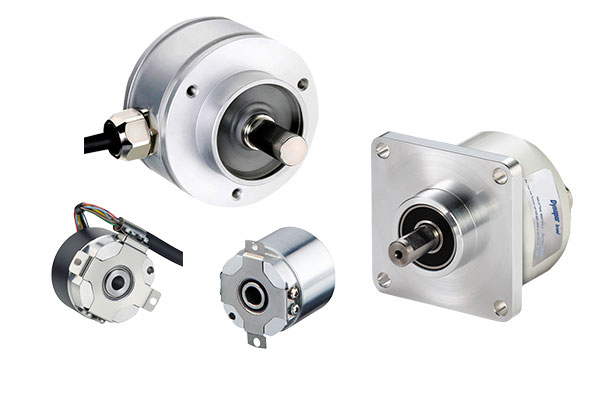
Encoder failure is most commonly attributed to bad bearings. Therefore, having a bearingless encoder eliminates that point of failure. Bearingless encoders are designed with magnetic technology that is less susceptible to dirt and moisture issues than bearings.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Magnetic Encoders
Hubshaft encoders are designed to allow the motor shaft to partially enter the encoder, saving space where it is limited.
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Installation
Shafted encoders are designed to be isolated from the motor for protection against shock and vibration and straight currents.
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder
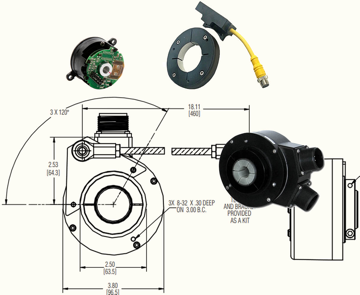
Hollowshaft encoders allow the motor shaft to pass completely through and are secured by a shaft collar. This mounting style is easier to install and requires less space than a shafted encoder. Flexibility from the tether allows the encoder to float with the movement of the motor shaft, alleviating wear and tear on the bearings. The shaft collar is electrically isolated from the motor for protection against stray motor current.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Absolute Encoders
There are several types of encoder mounting styles to choose from when selecting an encoder for your application. Typically, you will choose between hollowshaft, shafted, hubshaft, and ring (or c-faced) mounting styles for encoders. Hollowshaft encoders allow the shaft of the motor to go through the encoder, and secures to the shaft by the shaft collar. Shafted encoders attach to the motor with a flexible coupling or possibly a belt (gear). Hubshaft encoders mount to motor shafts similarly to hollowshaft encoders. The difference in the hubshaft is that the motor shaft can only go about halfway into the encoder rather than completely through. Lastly, the ring (c-faced) option allows the encoder to bolt directly to the flange of the motor for bearingless designs. You will need to choose the mounting style that best suits your motor or application.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Installation,
Absolute Encoders,
Optical Encoders,
Magnetic Encoders
Couplings mechanically and electrically isolate the encoder from the motor. This separation helps avoid encoder signal errors such as miscounts or extra counts by reducing noise in the encoder. In addition, electrical isolation prevents damage caused by current from the motor.
Couplings also allow the encoder to compensate for shaft misalignment. Cutouts on the coupling allow flex to occur in the coupling rather than in the motor shaft. The runout from the shaft is absorbed by the coupling to prevent physical damage to the encoder.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Installation,
Troubleshooting
Differential signals are not included in a single- ended output. This type of output will only provide A,B and Z signals. Single- ended outputs are common in older systems and can be more prone to noise than differential signals.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Encoder Signals Output
Reflective encoders produce signal based on the reflection of light. The motor shaft and encoder rotate in tandem. The code wheel has a pattern of reflective and non-reflective surfaces. As the light shines down on the rotating code wheel, it produces a predictable pattern of light and down. An internal sensor detects this pattern and produces digital pulse.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Encoder Signals Output
Magnetic encoders use a permanent magnet and a Hall Effect, or magnet resistive device, to produce a change in voltage or electrical resistance in the presence of ferromagnetic material. This change will occur in the form of a gear tooth (in a rotary encoder) or a metal band with slots (in a linear encoder). Tis type of sensor will work down to zero speed, and is available in both rotary and linear forms.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Encoder Signals Output,
Magnetic Encoders
Optical encoders use a glass disk with a pattern of lines deposited on it, a metal or plastic disk with slots (in a rotary encoder), or a glass or metal strip (in a linear encoder). Light from an LED shines through the disk or strip onto one or more photodetectors, which produce the encoder’s output. An incremental encoder has one or more of these tracks, while an absolute encoder has as many tracks as it has output bits.
Read More
Topics:
How to Choose An Encoder,
Encoder Signals Output,
Optical Encoders