Shafted Rotary Encoders
Dynapar offers a wide range of shafted rotary encoders that mount to a motor or driven shaft via a flexible coupling.
Learn More
Other Categories
Optical Rotary Encoders
Magnetic Rotary Encoders
Hollow-Shaft Encoders
Hub-Shaft Encoders
Shaft Encoders
Miniature Encoders
Hazardous Area Encoders
Non Contact Encoders
Bearingless Encoders
Ethernet Protocol Encoders
Service & Support Overview
Product Quicklinks
Competitor Parts List
Discontinued Encoder Guide
Literature Library
RMA Request
Technical Support
Product Manuals & Installation Guides
Knowledge Center
Technology
How to Choose Feedback
Application Examples
Case Studies
Encoder Issues and Troubleshooting
White Paper Downloads
Literature Library
Power Point Downloads
Videos
Featured Links
Motor Encoders
Quadrature Encoders
Optical Encoders
Magnetic Encoders
How to Specify a Resolver
Draw Wire Encoders
Hall Effect Encoders
Encoder Accuracy vs Resolution
A hall effect encoder uses a hall-array sensor passed over a magnetic field to produce a signal that is then interpolated to resolution. Dynapar hall effect magnetic encoders use a magnetic phased array sensor to average the signal over multiple detectors to deliver a robust, high resolution signal that is insensitive to misalignment, shock and vibration.
How Hall Effect Encoders Work
Hall effect encoders use magnetic phased arrays that contain hall sensor elements arranged in a pattern to match a magnetic wheel. A signal is produced as the sensor passes over the magnetic field which is then interpolated to the desired resolution. This magnetic phased array technology is now available in an IC Chip which integrates both the sensor and the processor in the same chip which considerably decreases the chip count and pc board complexity for a robust, compact, easily manufacturable component. Magnetic Hall Phased Array technology represents the leading edge magnetic encoder technology today.
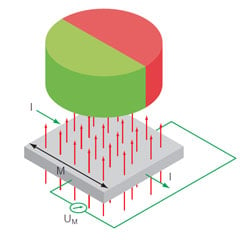
Diagram: Inside a magnetic hall effect encoder, a Hall-array sensor averages the signal over multiple detectors to deliver robust, high-resolution performance that is insensitive to misalignment, shock, and vibration.
The innovation of phased array technology has dramatically improved optical encoder technology. Similarly, magnetic phased array systems have benefited in the same way increasing resolution, compactness and reliability of magnetic encoder systems. Their designs spread data capture across multiple detectors, averaging out errors and increasing sensitivity.
Magnetic hall effect encoders can be extraordinarily robust. Because magnetic encoders are based on an inductive effect, they do not require bearings, which removes a point of failure from the system. Typically, the electronics inside the hall effect encoder are encapsulated so that they are not exposed to the elements. As a result, magnetic hall effect encoders can operate covered in dust in a sawmill or splashed daily in a washdown environment without any additional protection.
A magnetic hall effect encoder is designed to output reliable digital feedback in the most demanding and harshest of application environments. Applications for this technology usually require broad temperature specifications, high shock and vibration resistance, robust sealing, and contaminant protection all while focusing on output signal reliability, easy installation, and downtime reduction. Popular applications for magnetic hall effect encoders include speed and position feedback in construction, agriculture, mining, forestry and in food and beverage applications with wash downs or corrosive chemicals.
See all hall effect non contact encoders
See all heavy duty hall effect magnetic encoders
© Copyright Dynapar 2024 All Rights Reserved