- Industrial Encoder
- Motor Encoders
- Resolvers
- Incremental Encoders
- Absolute Rotary Encoders
- Magnetic Encoders
- Optical Shaft Encoders
- Optical Rotary Encoders
- Hollow-Shaft Encoders
- Quadrature Encoders
- Draw Wire Encoders
- Hall-Effect Encoders
- Hazardous Location Encoders
- Functional Safety Encoders
- Encoder Interface Protocols
- BiSS Encoders
- SSI Encoders
- Gray Code Encoders
- What is an Encoder?
- Electric Motor Controllers
- Types of Safety Encoders
Comprehensive Guide to Motor Encoders
If you're exploring motor control systems, you've likely come across the term "motor encoders." These devices are crucial for providing closed-loop feedback control, enabling precise management of motor speed and position. But what exactly are motor encoders, how do they work and why are they so vital? In this guide, we'll explain how motor encoders work, the various types available, and their importance in motor control systems.
This article will cover (click to jump to each section):
- What are Motor Encoders?
- Types of Motor Encoders
- Why You Need Motor Encoders
- How to Specify A Motor Encoder
What are Motor Encoders?

Motor encoders are rotary encoder measures the position and speed of a motor's shaft. They provide feedback to the motor control system, allowing it to adjust the motor's speed and position in real-time.
Types of Motor Encoders
Two motor encoder types exist: absolute encoder and incremental encoder.
Absolute Motor Encoders
Absolute encoders are essential for providing precise position information in motor control systems. They come in two main types
Single-turn absolute encoders:
-
- Generate a unique code for each position within a single revolution.
- Ideal for limited shaft rotation applications.
Multi-turn absolute encoders:
-
- Provide a unique code for each position within multiple revolutions.
- Suitable for continuous shaft rotation applications.
Absolute encoders ensure accuracy even after power loss or system shutdown, making them indispensable for applications demanding high precision and reliability. Contact us to explore our range of rotary encoders, tailored to your specific needs.
Incremental Motor Encoders
Incremental encoders are widely used in motor control systems to determine the motor's direction and number of steps taken. While they lack absolute position information, they offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Despite this limitation, incremental encoders excel in high-speed and high-accuracy applications, making them a preferred choice for various industrial applications.

HS35R Hollow-shaft Incremental Motor Encoder
Reliable Hollow-Shaft Encoder Offers Extreme Performance for Heavy Duty Applications
Customize & Buy Now- Up to 5000 PPR
- Optical Sensing
- Up to IP67

AD36 Absolute Hollowshaft Motor Encoder
1.5" OD Compact Hollow-Shaft Absolute Encoder with Up to 22 Bits ST and 12 Bit MT
Customize & Buy Now- Up to 22 bit ST, 12 bit MT
- Optical Sensing
- Up to IP40

HS35iQ Programmable Motor Encoder
Programmable Hollow Shaft Motor Encoder with Specific Fault Detection Capabilities
Customize & Buy Now- Up to 20,000 PPR
- Optical Sensing
- Up to IP67
Why You Need Motor Encoders
.png?width=300&height=257&name=encoders1%20(1).png)
Motor encoders are essential for any motor control system that requires high levels of accuracy and precision. You need to know the exact position and speed of a motor's shaft to achieve the necessary control. Motor encoders are commonly used in a range of applications, including:
- Robotics
- Automation
- Manufacturing
- Medical Devices
- Aerospace Systems and more
Whether you're looking for a motor encoder for a specific application or you're just interested in learning more about motor encoders, we're here to help. Contact us today to learn more about our range of motor encoders and how they can benefit your operations.
How to Specify A Motor Encoder
When selecting components for a closed-loop control system, the motor encoder choice is first determined by the type of motor chosen in the application. The most common motor types are:
- AC Motors Encoders
AC induction motors are popular choices for general automation machine control systems as they are economical and rugged. Motor encoders are used for more precise speed control in applications using AC motors and often times need to have more robust IP, shock and vibration parameters. - Servo Motor Encoders
Servo motors encoders (permanent magnet motor encoders) offer closed-loop feedback control systems to applications that require higher precision and accuracy and are less robust than AC induction motors. The motor encoder used on servo motors can be modular, incremental, or absolute, depending on the level of resolution and accuracy required. - Stepper Motor Encoders
Stepper motors are cost-effective, precise, and are typically used in open-loop systems. In systems using stepper motors where speed control is required, an incremental motor encoder is often mounted allowing the stepper motor system to achieve closed-loop feedback. Stepper motor encoders can also be used in some applications to allow for improved control of stepper motors by providing precision feedback of the location of the motor shaft in relation to the step angle. - DC Motor Encoders
DC motor encoders are used for speed control feedback in DC motors where an armature or rotor with wound wires rotates inside a magnetic field created by a stator. The DC motor encoder provides a mechanism to measure the speed of the rotor and provide closed-loop feedback to the drive for precise speed control.
Motor Encoder Mounting Options
The next factor impacting motor encoder selection is the mounting option, and the most common options are:
- Shafted Motor Encoders: Uses a coupling method to connect the motor encoder shaft to the motor shaft. The coupling provides mechanical and electrical isolation from the motor shaft but can add cost via the coupling and the longer shaft length required to mount the motor encoder.
- Hub/Hollow shaft Motor Encoders: Hollow shaft encoders directly mount to the motor shaft via a spring-loaded tether. This method is easy to install and requires no shaft alignment, but proper care must be taken to provide electrical isolation.
- Bearingless Motor Encoders: Also known as ring mount, this mounting option comprises a magentic sensor assembly in the form of a ring mounted on the motor face and a magnetic wheel mounted on the motor shaft. This type of motor encoder mounting configuration is mostly found in heavy-duty applications like paper, steel, and cranes
- .
Find The Right Motor Encoder for Your Application
Use our selection tool to narrow down your search
Step 1: Select Feedback Type (Learn How to Choose)
Absolute Motor Encoders
Incremental Motor Encoders
Step 2: Select Mounting Style (Learn How to Choose)
Hollow Shaft Motor Encoders
Hub Shaft Motor Encoders
Shafted Motor Encoders
Step 2: Select Mounting Style (Learn How to Choose)
Hollow Shaft Motor Encoders
Hub Shaft Motor Encoders
Shafted Motor Encoders
Looking for a Custom Solution?
Tell us your requirements and our application engineers will help find the right solution today.
Contact Us →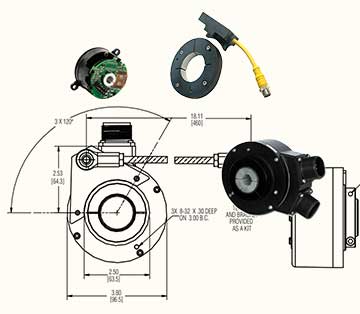



 {{else if (myEq content.heading "Absolute Encoders")}}
{{else if (myEq content.heading "Absolute Encoders")}}
 {{/if}}
{{/if}}