- Industrial Encoder
- Motor Encoders
- Resolvers
- Incremental Encoders
- Absolute Rotary Encoders
- Magnetic Encoders
- Optical Shaft Encoders
- Optical Rotary Encoders
- Hollow-Shaft Encoders
- Quadrature Encoders
- Draw Wire Encoders
- Hall-Effect Encoders
- Hazardous Location Encoders
- Functional Safety Encoders
- Encoder Interface Protocols
- BiSS Encoders
- SSI Encoders
- Gray Code Encoders
- What is an Encoder?
- Electric Motor Controllers
- Types of Safety Encoders
Gray Code Encoder Overview
What are Gray code encoders? Also known as reflected binary code encoders, gray code encoders are designed to enhance accuracy and reduce communication errors by changing only one bit at a time. Ideal for serial and parallel communication protocols, gray code ensures reliable data transmission in various applications. Learn more about the benefits and top-rated gray code encoders for your system needs.
Gray Code Encoder Output vs Binary Output
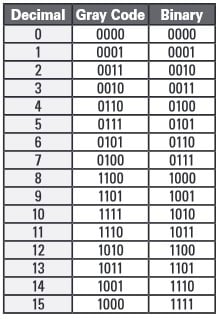
Parallel encoder output delivers a rapid stream of bits. When the data is in binary format, multiple bits can change per step, and in some cases, all bits may alter between each read. In high-speed applications, this can lead to errors or complex programming challenges. Gray code minimizes the bit change to just one data bit per measurement step.
Table: Example of conversion between straight binary and gray code encoder output.
Gray Code Encoder Applications
Gray code rotary encoders are used in various applications where precise position measurement and minimizing errors are crucial. Here are some typical applications:
- Industrial Automation: Gray code rotary encoders are widely used in industrial automation to accurately determine the position of machinery and robotic arms, ensuring precise control and operation
- Robotics: In robotics, gray code encoders help in tracking the position and movement of robotic joints and wheels, providing reliable feedback for navigation and manipulation tasks
- CNC Machines: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines use gray code rotary encoders to monitor the position of cutting tools and workpieces, ensuring high precision in manufacturing processes
- Medical Equipment: Gray code encoders are used in medical devices, such as imaging equipment and surgical robots, to provide accurate positioning and movement control
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, gray code rotary encoders are employed in various systems, including flight control surfaces and satellite positioning, to ensure precise and reliable operation
These applications benefit from gray code's unique property of changing only one bit at a time, which minimizes the risk of errors during state transitions.
Is there a specific application you're interested in learning more about?
Parallel Output Encoders
Parallel output makes all output bits available simultaneously. It may be provided as straight binary or transformed into gray code to reduce errors.
The advantage of parallel output is that it’s fast: all the data is available in real time, all the time. Disadvantages include bulky (and expensive) cables and limited cable length. Most encoders come with cables a meter or two long, but a parallel output using differential output (push-pull) and shielded cabling can be extended to 100 m using a thicker cable, at a reduction in speed. Open-collector (sinking or sourcing) outputs can go roughly a third that far.
Serial Output Encoders
The alternative to parallel communication is serial. SSI requires less cabling for data transfer, the same interface hardware regardless of the absolute encoder’s resolution and less electronic components.
There are several dedicated serial buses available including SSI and BiSS, as well as standard industrial buses including DeviceNet, CAN Bus, Profibus and Interbus. Tradeoffs among these include bandwidth, update rate, hardware requirements, wire count, proprietary vs. nonproprietary nature, and availability.
Looking for a Custom Solution?
Tell us your requirements and our application engineers will help find the right solution today.
Contact Us →
 {{else if (myEq content.heading "Absolute Encoders")}}
{{else if (myEq content.heading "Absolute Encoders")}}
 {{/if}}
{{/if}}