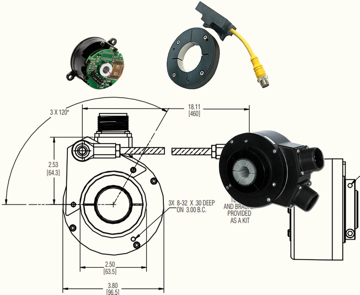
Building the Right Foundation with a Hollow Shaft Encoder
Every rotary encoder works by being mounted to a motor by a shaft. The encoder has a fixed housing with a rotor wheel (either a detached component or integrated within the housing with bearings) which revolves around the shaft. Those rotations are the basis for determining speed, positioning, and other motion information.
The single most important thing that distinguishes encoder designs is the mounting configuration. The inner workings of the encoder may all be the same – absolute or incremental, optical or magnetic – but, the simple decision on how to attach the encoder can make a major difference in the physical design of your application.
A hollow shaft encoder mount is one of the lowest-overhead, lowest-stress options for an encoder. This design offers simplicity because a hollow shaft encoder is compact, adjustable, and versatile.
Dynapar's Most Popular Hollow Shaft Encoders



View all hollow-shaft encoder models here
From Basic Solid Shafts to Hollow Shaft Encoder Mounts
The original encoder design used a solid shaft. As the name implies, a solid shaft encoder has a solid bar that 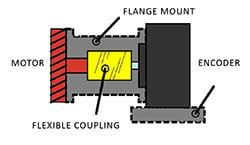 attaches to the motor and is attached using a flexible coupling and an external flange. There are some limitations with this design, specifically with the fact that the shaft requires an exact width and length to the shaft to fit into the motor and that it requires two external pieces (the flex couple and flange), which add to the size of the encoder. Solid shaft encoders are also susceptible to misalignment, which can impair performance.
attaches to the motor and is attached using a flexible coupling and an external flange. There are some limitations with this design, specifically with the fact that the shaft requires an exact width and length to the shaft to fit into the motor and that it requires two external pieces (the flex couple and flange), which add to the size of the encoder. Solid shaft encoders are also susceptible to misalignment, which can impair performance.
Since the original solid shaft design, more mounting options have come around, like direct mounts and a C-face or ring mount. These have benefits – like the easier installation of direct mounts or the bearingless C face-mounts which reduce wear. However, these designs also have drawbacks, particularly in how difficult these designs are to install or in the overall size of the encoder profile.
A hollow shaft encoder is one of the most common shaft designs because of its versatility. Instead of having a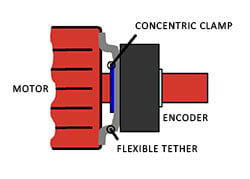 solid bar that has to match the motor, a hollow shaft encoder fits over the motor shaft and is then clamped in place. It’s held in position by a flexible tether. This means that a hollow shaft encoder does not have to be perfectly sized to fit the motor and it does not require any external components which increase its size. A hollow shaft encoder also has a more forgiving installation; the clamp and the tether can be used to adjust the position and to absorb shocks and vibration that could cause misalignment.
solid bar that has to match the motor, a hollow shaft encoder fits over the motor shaft and is then clamped in place. It’s held in position by a flexible tether. This means that a hollow shaft encoder does not have to be perfectly sized to fit the motor and it does not require any external components which increase its size. A hollow shaft encoder also has a more forgiving installation; the clamp and the tether can be used to adjust the position and to absorb shocks and vibration that could cause misalignment.
Hollow Shaft Encoder in Summary
A hollow shaft encoder design offers simplicity to the application:
- More forgiving shaft sizing, especially in length
- Easier installation, positioning, and alignment
- Moderate resistance against shock and vibration
- Smaller installation profile, without extra coupling
- Good foundation for speed and RPM feedback
A hollow shaft encoder provides a strong, environment-tolerant style that is ideal for industrial duty applications. In fact, a hollow shaft encoder design is the most preferred style for speed feedback in industrial applications because of its reliable performance.
There are many options for mounting an encoder, and your environment should dictate what style to get. A hollow shaft encoder is the best choice for an environment where speed is a crucial information factor, size and simplicity are integral to the application design, and the environment can face contaminants like shocks, moisture, or particulates




 attaches to the motor and is attached using a flexible coupling and an external flange. There are some limitations with this design, specifically with the fact that the shaft requires an exact width and length to the shaft to fit into the motor and that it requires two external pieces (the flex couple and flange), which add to the size of the encoder. Solid shaft encoders are also susceptible to misalignment, which can impair performance.
attaches to the motor and is attached using a flexible coupling and an external flange. There are some limitations with this design, specifically with the fact that the shaft requires an exact width and length to the shaft to fit into the motor and that it requires two external pieces (the flex couple and flange), which add to the size of the encoder. Solid shaft encoders are also susceptible to misalignment, which can impair performance. solid bar that has to match the motor, a hollow shaft encoder fits over the motor shaft and is then clamped in place. It’s held in position by a flexible tether. This means that a hollow shaft encoder does not have to be perfectly sized to fit the motor and it does not require any external components which increase its size. A hollow shaft encoder also has a more forgiving installation; the clamp and the tether can be used to adjust the position and to absorb shocks and vibration that could cause misalignment.
solid bar that has to match the motor, a hollow shaft encoder fits over the motor shaft and is then clamped in place. It’s held in position by a flexible tether. This means that a hollow shaft encoder does not have to be perfectly sized to fit the motor and it does not require any external components which increase its size. A hollow shaft encoder also has a more forgiving installation; the clamp and the tether can be used to adjust the position and to absorb shocks and vibration that could cause misalignment.